PFAS Waste Management for Safer Disposal and Environmental Protection
PFAS Waste Management for Safer Disposal and Environmental Protection
Blog Article
Your Guide to PFAS Treatment Technologies and Conveniences
The frequency of PFAS contamination in water resources demands a thorough understanding of offered treatment modern technologies. Each modern technology not just targets particular PFAS substances yet likewise plays a critical function in boosting general water quality and protecting ecological integrity.
Understanding PFAS Contamination
Comprehending PFAS contamination is vital for addressing its pervasive influence on environmental and human health and wellness (m270 pfas treatment). Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) are a team of artificial chemicals commonly used in numerous industrial and consumer items because of their water- and grease-resistant residential properties. Typically discovered in firefighting foams, non-stick cooking equipment, and water-repellent fabrics, PFAS have gone into the setting via manufacturing procedures, wastewater discharges, and leaching from garbage dumps
As soon as released, these substances continue the environment, causing extensive contamination of dirt and water resources. Their distinct chemical structure, characterized by strong carbon-fluorine bonds, makes them resistant to degradation, causing a phenomenon known as "permanently chemicals." Subsequently, PFAS can build up in the body and the food cycle, possibly creating unfavorable health impacts, including immune system disruption, developmental concerns, and a boosted danger of specific cancers cells.
Governing agencies and health companies are significantly recognizing the value of PFAS contamination, motivating initiatives to monitor, examine, and minimize its impacts. Understanding the paths of PFAS contamination is essential for informing public law and developing reliable methods to protect both environmental and human health.
Summary of Therapy Technologies
Various therapy technologies have been developed to address the challenges positioned by PFAS contamination in water and soil. These technologies can be broadly categorized right into a number of categories, each with its unique mechanisms and performance in getting rid of PFAS substances.
One famous technique is ion exchange, which uses material materials to catch and eliminate PFAS from polluted water. Another innovation, progressed oxidation processes (AOPs), employs strong oxidants and ultraviolet light to break down PFAS into less hazardous substances.
Activated Carbon Purification
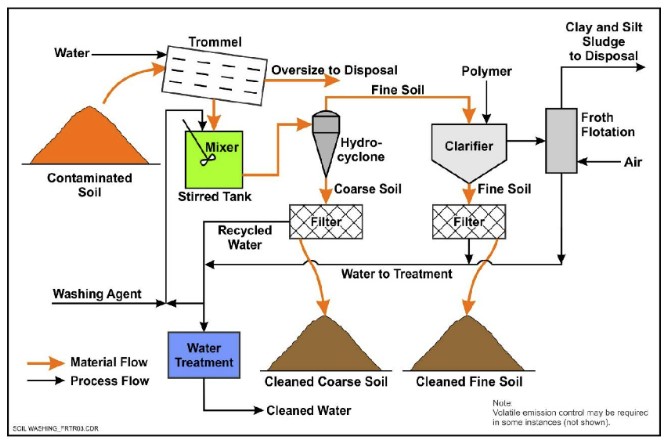
Turned on carbon filtering is an extensively utilized method for the removal of PFAS from polluted water, known for its ability to adsorb a wide array of organic compounds. This modern technology utilizes activated carbon, a very porous material with an extensive area, which assists in the binding of PFAS particles through physical adsorption. The effectiveness of activated carbon in removing PFAS is affected by numerous variables, consisting of the kind of carbon utilized, the call time, and the focus of PFAS in the water.
Among the advantages of activated carbon purification is its flexibility; it can be applied in various arrangements, such as granular triggered carbon (GAC) systems or powdered triggered carbon (PAC) systems. GAC systems are usually employed in larger-scale applications, while political action committee can be utilized in smaller sized or momentary setups. Moreover, the modern technology is relatively simple to operate and preserve, making it obtainable for numerous water treatment centers.
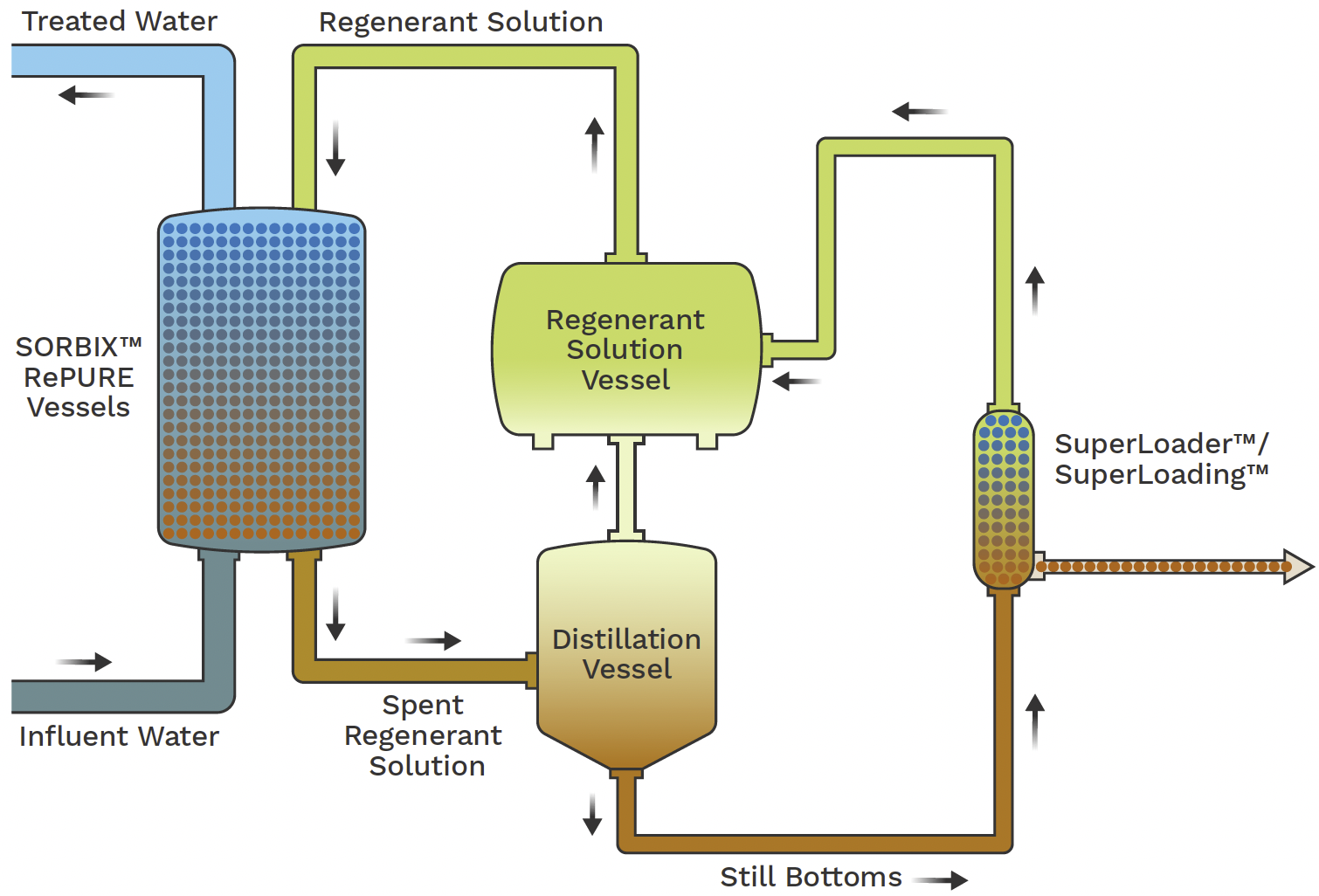
Ion Exchange Equipment
Ion exchange systems stand for one more efficient strategy for the removal of PFAS from polluted water, enhancing approaches like activated carbon filtration. These systems operate on the principle of exchanging ions in the water with ions hung on a resin product. Ion exchange materials can be particularly formulated to target the adversely billed PFAS compounds, efficiently recording them and allowing cleaner water to travel through.
Among the main benefits of ion exchange systems is their capability to eliminate a vast array of PFAS, including both long-chain and short-chain variants. This adaptability Extra resources makes them ideal for different applications, varying from local water therapy to industrial processes. Furthermore, ion exchange systems can often attain lower detection limits for PFAS compared to some other treatment methods, thus enhancing water high quality.
Nonetheless, it is vital to keep an eye on and manage the regeneration of ion exchange media, as the efficiency can decrease gradually due to saturation. Appropriate upkeep and substitute of the material are essential for sustaining the system's performance. On the whole, ion exchange systems supply a trusted and efficient solution for PFAS elimination, contributing substantially to safe drinking water requirements and ecological security.
Advanced Oxidation Processes
Advanced Oxidation Processes (AOPs) use powerful oxidants to successfully break down PFAS compounds in polluted water. These cutting-edge treatment techniques create very reactive find types, such as hydroxyl radicals, that can break down intricate PFAS molecules into less unsafe by-products. m270 pfas treatment. AOPs normally use combinations of ultraviolet (UV) light, ozone, hydrogen peroxide, or Fenton's reagent, enhancing the oxidation capacity and enhancing destruction efficiency
The key advantage of AOPs depends on their capacity to target a broad series of PFAS substances, consisting of both long-chain and short-chain variants. This adaptability is vital, as PFAS contamination usually includes mixes of different substances with varying chemical structures. AOPs can be integrated into existing water therapy systems, making them a functional solution for several communities and sectors.
Nevertheless, the execution of AOPs can be resource-intensive, needing mindful consideration of operational prices and energy intake. Furthermore, while AOPs work in damaging down PFAS, they may not completely get rid of click site all results, requiring additional treatment actions - m270 pfas treatment. On the whole, AOPs represent a promising avenue for attending to PFAS contamination, adding to cleaner water resources and improved public health protection

Final Thought
By selecting the suitable technology, neighborhoods can boost water top quality, safeguard public health, and mitigate the environmental threats linked with PFAS direct exposure. Proceeded research and application of these approaches are important for effective management of PFAS contamination in affected areas.
Report this page